- Home
- Product Reviews
- Rogaine Side Effects
Rogaine Side Effects in Men and Women: Tingling Sensation? Low Libido? Forehead Rash?
By Paul Taylor
Who’s more likely to suffer Rogaine side effects, men or women? And what are all these side effects anyway?
The
answers should help you decide whether or not to try this drug or opt for
a safer alternative approach.
The Side Effects of Rogaine
Most men and women with hair loss know that Rogaine (Regaine in the UK) is a brand name for minoxidil, a drug approved by the FDA to treat this condition after trials showed it can stimulate hair regrowth.
But although minoxidil has been scientifically proven to regrow hair, it’s also been scientifically proven to cause side effects.
Here are all the potential side effects listed in increasing order of severity, mild, moderate and severe:
Mild side effects
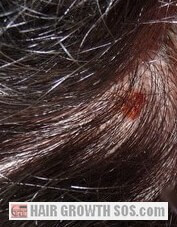
- Inflammation of your hair follicle roots.
- A dry, flaky, itchy scalp.
- Spots (acne) developing on your scalp.
- A numb or tingling sensation in your hands, feet, or face.
- The very fine (near invisible) vellus hairs on your body could start growing* into mature terminal hairs.
*
Whilst such an increase in hair growth might initially sound like a
benefit, you wouldn’t be too impressed if the tiny vellus hairs on your
nose or forehead started to sprout out thicker, longer and darker. And, for women especially, terminal hair growth on the face or body would be extremely undesirable.

Moderate side effects
- A burning or tingling sensation in your scalp.
- Skin may start to show a reddened appearance or rash (e.g., on your forehead).
- Breast tenderness.
- Low libido.
- Light-headedness
(all antihypertensive drugs like minoxidil can cause this through a
sudden drop in blood pressure).
- Swelling
- An increase in water retention can cause your face, hands, feet or
lower legs to swell up.
- An increase in hair loss*.
* It sounds bizarre, and it is. Rogaine can make your hair loss worse. Initially at the very least. Minoxidil is used for treating hair loss, but can shift more hair follicles into the resting phase of the hair growth cycle, so you might start shedding even more hair (1).
Serious side effects
- Rapid weight gain.
- An upset stomach or vomiting.
- Headaches.
- Blurred vision.
- Fainting.
- Rapid heartbeat or heart palpitations.
- Chest pain (angina).
- Breathing problems.
It's very easy to dismiss the more serious Rogaine side effects simply because they only develop very rarely in just a few people. But some of these problems are entirely possible, especially if you discover you have an
allergy to minoxidil or one of the other ingredients such as
alcohol and propylene glycol (1).

Some side effects of Rogaine are more common than others of course. A dry, flaky, itchy scalp being the most likely, and an allergic reaction (which then causes some of the more serious side effects) the least.
But obviously it goes without saying that you would need to contact a doctor
urgently if you experience any symptom you consider serious.
Are Men or Women More Likely to Suffer Rogaine Side Effects?
Rogaine is available in two concentrations - a regular 2% strength liquid product is suitable for women, and an "Extra Strength" 5% liquid product is suitable for men only (women could start growing facial hair if they use it). Rogaine can also be applied as a 5% strength foam. Initially, this was for men only, but a 5% foam product for women is now available as well.
So it seems likely that men who use the liquid product might be more likely to suffer side effects simply because their (5%) liquid product is much stronger than the liquid product for women (2%).
As for the foam product, it might be easier (for both men and women) to overdose from the recommended amount - "half a cap" of foam twice a day sounds a bit vague to me, especially when compared to the liquid which comes with a dropper to accurately measure two 1 ml doses per day.

But if minoxidil does start changing the tiny vellus hair on the face and body into mature terminal hair, this side effect would probably be more of an issue for women than it is for men.
Clearly then, you would need to be very careful not to get minoxidil on your skin (including your nose, forehead, face, etc) and wash your hands thoroughly every time you use it.
Note: Another reason why you need to wash your hands thoroughly is because the high alcohol content also makes Rogaine products highly flammable.
Some
of the side effects you could experience depend on how quickly the drug
gets absorbed by your body - something which can vary from person to person. So that would explain why some people might be adversely affected simply from using the
recommended daily dose. And it would explain why Rogaine might help some people to grow hair but not many others.
Summary About Using This drug
To sum up:
- Try Rogaine and you might suffer mild to moderate side effects (about 4% of people) or even severe side effects if you’re really unlucky.
- You’ll need to use it for months before you know whether Rogaine works for you, or if
it’s been a complete waste of your time, effort and money.
- You could very well suffer even more hair loss as a direct result of using this drug. The duration all this extra shedding lasts
can obviously vary from person to person – so you might have to
endure weeks of extra hair loss.
- Whilst the manufacturer will
refund any unopened Rogaine product you return to them (minus all your
postage costs), there’s no guarantee from them that all this extra hair
loss will be replaced with hair regrowth.
- If Rogaine does work for you,
you'll have to keep using it for life, during which time, any mild or
moderate side effects you experience could accumulate and develop into
something more serious.
- Even if you do notice some beneficial effects, this might not be any
more than minimal hair regrowth at best.
Final Notes
There are many types of hair loss. Minoxidil treatment is intended for hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia.
Although "Men's Rogaine" and "Women's Rogaine" (formerly "Rogaine for Men" and "Rogaine for Women") are the most well known brand names, Rogaine isn't the only product that delivers minoxidil to your scalp. Generic versions of minoxidil are also available.
Final page: Generic Rogaine.
Sources of Rogaine side effects include: webmd.com and mayoclinic.com.
|
Like this page? |
|


Comments and Questions?
Comments and questions about the page you just read are welcome. Just post in the box below. Please also observe the Commenting Rules (opens in a new window).